
(with distinction) in Computational Linguistics from the University of Tübingen in 1998, conducted post-doctoral work at Brown University in 1999, and spent a decade in industry research (Xerox PARC, Google Research). Stefan Riezler is full professor at the Department of Computational Linguistics at Heidelberg University, Germany, since 2010, and also co-opted in Informatics at the Department of Mathematics and Computer Science. The book is self-contained, with an appendix on the mathematical background on GAMs and LMEMs, and with an accompanying webpage including R code to replicate experiments presented in the book. This book can be used as an introduction to empirical methods for machine learning in general, with a special focus on applications in NLP and data science.

Last, a significance test based on the likelihood ratio of nested LMEMs trained on the performance scores of two machine learning models is shown to naturally allow the inclusion of variations in meta-parameter settings into hypothesis testing, and further facilitates a refined system comparison conditional on properties of input data. Furthermore, the book discusses a reliability coefficient using variance decomposition based on random effect parameters of LMEMs. Based on the interpretable parameters of the trained GAMs or LMEMs, the book presents model-based statistical tests such as a validity test that allows detecting circular features that circumvent learning. Our focus is on model-based empirical methods where data annotations and model predictions are treated as training data for interpretable probabilistic models from the well-understood families of generalized additive models (GAMs) and linear mixed effects models (LMEMs).

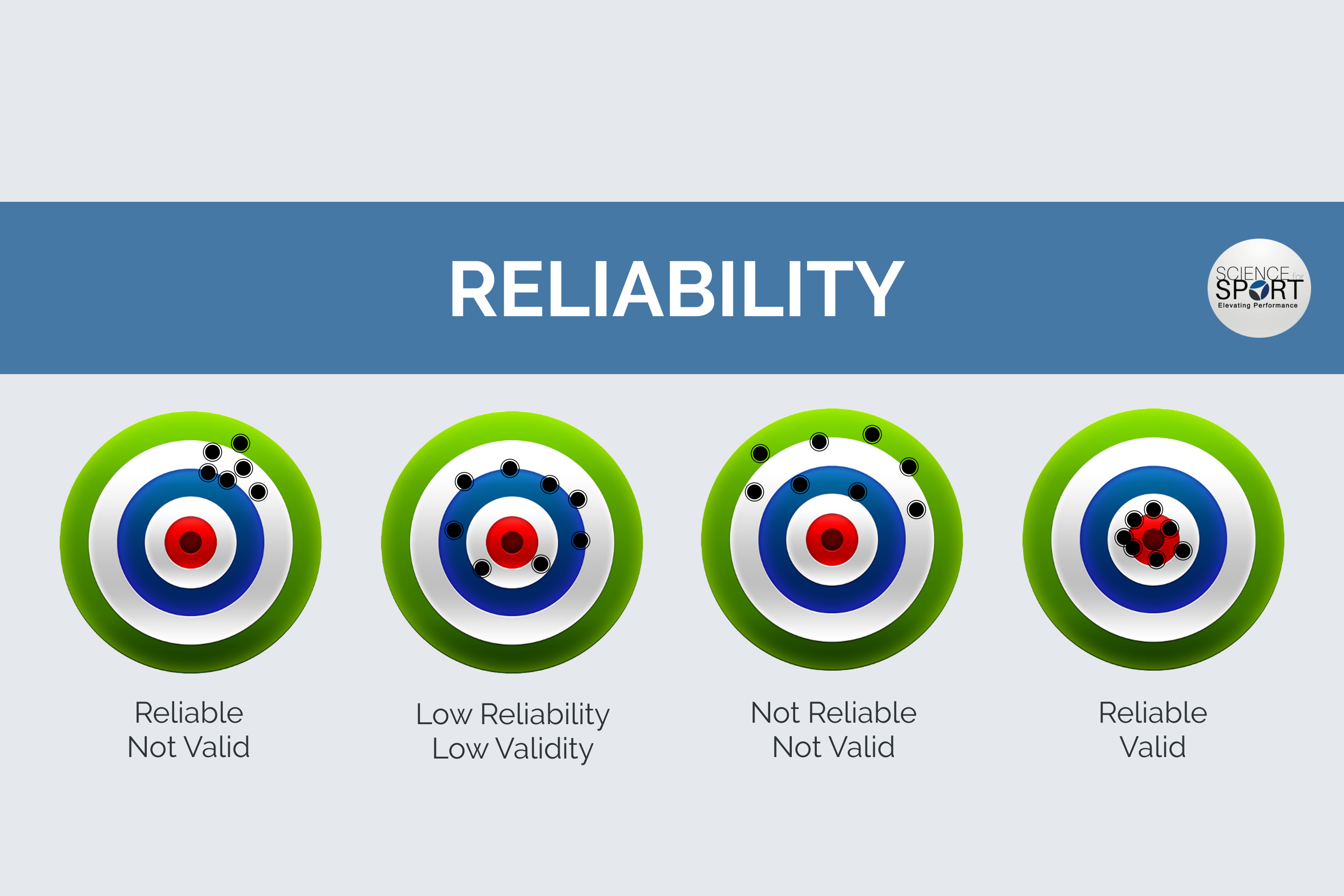
The goal of this book is to answer these questions by concrete statistical tests that can be applied to assess validity, reliability, and significance of data annotation and machine learning prediction in the fields of NLP and data science. In the case of machine learning, these correspond to the questions of whether a model predicts what it purports to predict, whether a model's performance is consistent across replications, and whether a performance difference between two models is due to chance, respectively. The methodological questions addressed in this book include the problems of validity, reliability, and significance. Empirical methods are means to answering methodological questions of empirical sciences by statistical techniques.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
